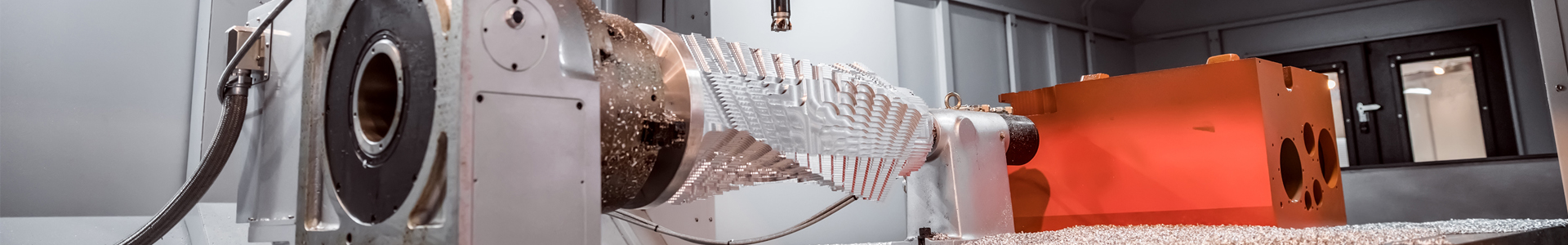
In the process of machining, it is often difficult to use standard tools for machining. It is very important to manufacture non-standard tools. Because the use of non-standard tools in metal cutting is common in milling, this paper mainly introduces the manufacture of non-standard tools in milling.
Because the purpose of manufacturing standard tools is to cut a large number of general metal and non-metallic parts in a large area, when the workpiece becomes hard due to overheating, the workpiece is made of stainless steel, and the cutting edge is very easy, and there is also the surface of the workpiece. When the geometric shape is very complex or the roughness of the machined surface is very high, the standard tool cannot meet the processing requirements. Therefore, in the process of machining, the target design such as tool material, blade shape and geometric angle can be carried out, which can be divided into special orders and non-special orders.
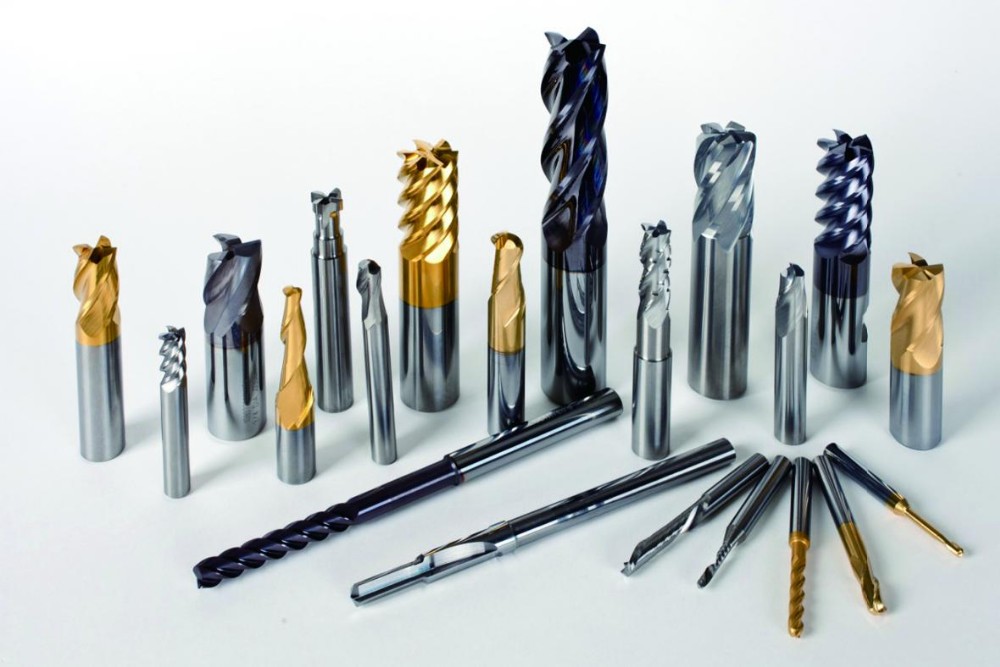

1、 Non-customized tools mainly solve two problems: size and surface roughness
(1) Size problem
You can select a standard tool with the same size as you need, which can be solved by regrinding, but two points need to be noted:
1. If the size difference is too large, the groove shape of the tool will change, directly affecting the chip removal space and geometric angle, so the size difference is not less than 2mm.
2. If it is a cutting machine without a cutter hole, it cannot be done with ordinary machine tools. It needs to be done with a special 5-axis connecting rod. The cost of changing machine tool grinding is also high.
(2) Surface roughness problem
This can be achieved by changing the geometric angle of the blade. For example, increasing the front and rear corners can significantly improve the surface roughness of the workpiece. However, if the user's machine tool is not rigid enough, the edge will become blunt and the surface roughness can be improved. This is very complex, and the treatment plant needs to be analyzed before any conclusion is reached.
2、 The tool to be customized is mainly to solve three problems: special shape, special strength and hardness, special tool tip tolerance and tool tip removal requirements
(1) Workpieces have special shape requirements
For example, the tool required for machining may be lengthened, the end teeth may be inverted, and there may also be special taper angle requirements, tool shank structure requirements, and edge length dimension control. If the geometric requirements of this tool are not very complex, it is actually easy to solve. The only thing to note is that non-standard tools are more difficult to handle. The pursuit of high precision means high cost and high risk, which will cause unnecessary waste to manufacturers' production capacity and their own costs.
(2) Strength and hardness of workpiece
When the workpiece is overheated, the common tool material for machining is too strong, too hard, or the tool is seriously worn. It needs to be transferred with special requirements for the material of the tool. The common solution is to select high-grade tool materials, such as high-speed steel tools with high hardness cobalt for cutting quenched and tempered workpieces, and high-quality cemented carbide. Machine replaces grinding. Of course, it can also be very special. For example, when machining aluminum parts, it may not match the type of commercially available carbide tools. Aluminum parts are generally soft, but can be easily processed. The material used for hard tools is actually an aluminum high-speed steel. Although this material is harder than ordinary high-speed steel, it will cause the affinity of aluminum elements and increase tool wear when machining aluminum parts. At this time, if you want to obtain high efficiency, you can choose cobalt high-speed steel instead.
(3) Workpieces have special requirements for blade tolerance and blade removal
In this case, a smaller number of teeth and deeper tooth tip grooves must be used, but this design can be used for mechanically simple materials, such as aluminum alloy.
In the design and processing of non-standard tools, the geometric shape of the tool is relatively complex, and bending deformation, deformation and local stress concentration are easy to occur during the heat treatment process, which must be avoided during the design. For parts with concentrated stress, bevel transition or ladder design shall be added for parts with large diameter variation.
If it is a slender piece with large length and diameter, it needs to be checked and straightened after each fire extinguishing and tempering to control the deformation and loss during heat treatment. The tool material is brittle, especially the hard alloy material. If the vibration is large or the processing torque is large, the tool will be damaged. If the tool is broken, it can be replaced, but in many cases it will not cause too much damage. However, when dealing with non-standard tools, the possibility of replacement is high, so once the tool is broken, it will cause great losses. Users, including a series of problems such as delay.