Brass, bronze, and copper belongs to the same group called Red Metals. While the three share some similarities, and some distinct differences that make them useful in different ways.
This article brings you a detailed comparison that will establish the difference between brass, bronze, and copper. It also outlines their distinct features, available alloys, applications, and many more. The information here will help you make the best metal choices for your metal projects.

1. Appearance and Touch

Each of these metals has a distinct appearance and feel. Copper has a reddish-brown color that can develop a green patina over time, while brass has a yellowish-gold color and can come in a polished or brushed finish. Bronze has a brownish-red color that can also develop a green patina over time.
In terms of texture, copper is smooth and cool to the touch, while brass is smooth and warm to the touch. Bronze has a slightly grainy texture and may feel warmer or cooler depending on the surrounding environment. Overall, each metal has a unique appearance and tactile sensation that can be appealing in different ways.
2. Composition Differences
Copper, brass, and bronze are all alloys made primarily of copper with varying amounts of other metals. The following table shows the composition differences between the three:
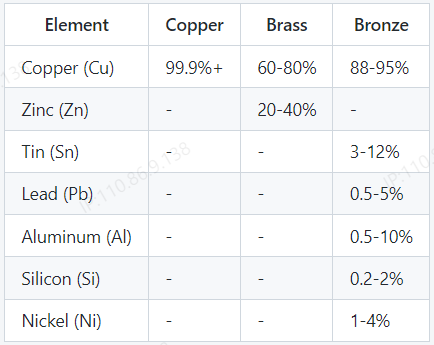
As shown in the table, brass is typically composed of copper and zinc, while bronze is typically composed of copper and tin, sometimes with additional elements such as lead, aluminum, silicon, or nickel.
Copper, on the other hand, is a pure element and not an alloy, meaning it contains only copper atomic constituents.
The different element compositions give each of these materials different mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties, making them useful for various applications.
3. Corrosion Resistance
Copper, brass, and bronze are all copper alloys that provide different levels of corrosion resistance.
Copper is highly resistant to corrosion due to its natural ability to form a protective layer of surface oxidation. This layer, known as a patina, protects the underlying copper from further corrosion. Copper is commonly used in plumbing and electrical applications due to its resistance to corrosion.
Bronze is an alloy of copper, tin, and sometimes other elements. Bronze is generally more corrosion-resistant than brass due to the presence of tin. This makes bronze particularly suitable for marine applications, such as propellers and boat fittings.
Brass is an alloy of copper, zinc, and sometimes other elements. The corrosion resistance of brass depends on the amount of zinc in the alloy. Brass with higher zinc content tends to be more corrosion-resistant. However, brass can still corrode when exposed to certain environmental conditions, such as saltwater.
In summary, the level of corrosion resistance of the 3 metals is copper>bronze>brass
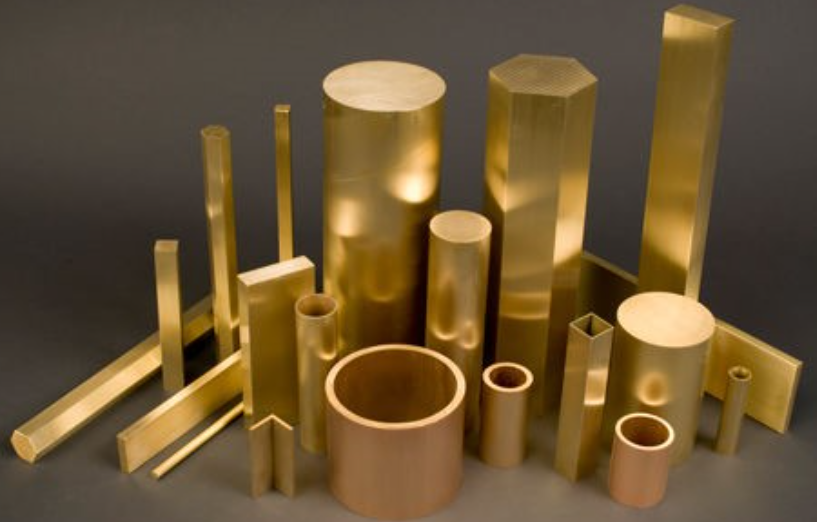

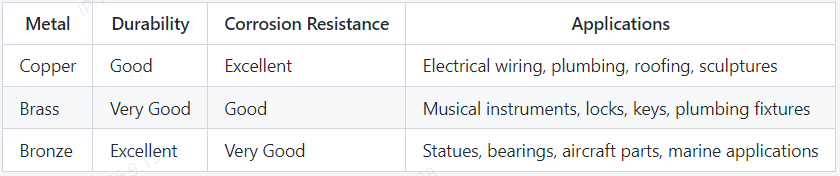
4. Durability & Applications
Durability is a measure of how resistant a material is against wear and tear over time. Corrosion resistance is a measure of how well a material resists damage caused by exposure to air, water, and other environmental factors.

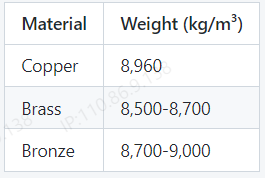
5. Weight Comparison
Overall, copper is the densest of the three materials, followed by brass and then bronze.
6. Hardness & Machinability
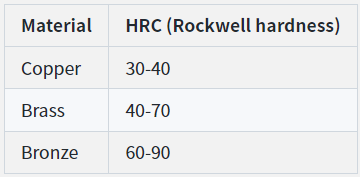
Copper scores 30 to 40 on the Rockwell hardness scale, while brass scores between 40 and 70. On the other hand, bronze has a score between 60 and 90. This result shows that bronze is the hardest of the three metals. In addition, it is more brittle and prone to fracturing.
Copper is generally considered to be a difficult material to machine due to its high ductility and softness.
Brass is easier to machine than copper due to its higher zinc content, which makes it less ductile. Bronze can be machined with moderate difficulty due to its hardness and abrasiveness. It is commonly used in machining operations, such as turning, drilling, and milling.
Bronze has fair machinability due to its hardness and brittleness. It can be difficult to cut and shape, but with proper tooling and machining techniques, it can be machined effectively.

7. Weldability
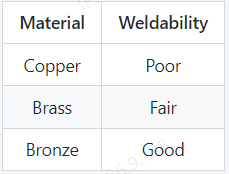
Generally, copper has poor weldability due to its high thermal conductivity, which leads to rapid heat dissipation, making it difficult to achieve proper fusion.
Brass has slightly better weldability than copper due to the addition of zinc, which lowers the melting point and makes it easier to weld using certain techniques such as brazing.
Bronze, on the other hand, has good weldability due to the presence of tin, which forms a lower melting point eutectic with copper, facilitating welding. However, all three materials require precise control of the welding process to achieve successful welds.
8. Electrical Conductivity
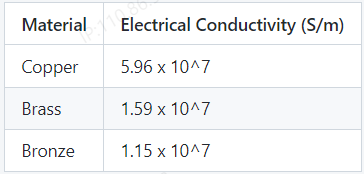
Copper, brass, and bronze are all alloys of copper with different compositions. Electrical conductivity is a measure of a material's ability to conduct electric current. Copper is the most conductive of the three materials, followed by brass and bronze.
Copper: Copper has high electrical conductivity due to its atomic structure and valence electrons. It is considered the standard for electrical conductivity and has a value of 100% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard). Pure copper wires are commonly used in electrical wiring and electronic components.
Brass: Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, with typically 60-70% copper content. The exact composition of brass affects its electrical conductivity. Generally, brass has lower conductivity than pure copper due to the presence of zinc atoms, which increase its resistance. However, some types of brass like Admiralty brass can have electrical conductivity comparable to pure copper.
Bronze: Bronze is an alloy of copper and other metals such as tin, aluminum, or nickel. The electrical conductivity of bronze varies depending on its composition. Usually, bronze has lower electrical conductivity than copper due to the presence of non-conductive metals. However, some types of bronze such as phosphor bronze can have relatively high conductivity due to the addition of phosphorus which enhances its electrical properties.
9. Thermal Conductivity
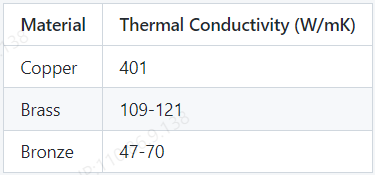
If you are looking for a material with high thermal conductivity, then copper would be the ideal choice. However, if your application does not require such high thermal conductivity, brass and bronze can also be suitable alternatives, depending on their specific range of thermal conductivity needs.
9. Tensile Strength and Yield Strength
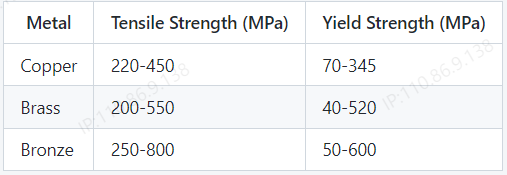
Tensile strength refers to the amount of stress a material can withstand before it fractures, whereas yield strength is the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically.
If you need a material with high strength characteristics, bronze would be the best option. Copper could be a good option if you need a balance between strength and flexibility, and brass could be used in situations where low strength is not a concern.
10. Ability to Form
Copper, brass, and bronze are all metals that can be formed into various shapes through different processes such as casting, forging, rolling, and extrusion. These three metals have different formability characteristics based on their composition, properties, and microstructure.
Copper:
Copper is known for its excellent malleability and ductility, which makes it easy to deform into different shapes without cracking or breaking. Copper can be easily rolled, drawn, hammered, or stamped into thin sheets, wires, or tubes. The high ductility of copper also allows it to be cold worked or hot formed with ease. However, copper is not suitable for deep drawing or complicated forming operations due to its low tensile strength and tendency to work harden quickly.
Brass:
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, which gives it better tensile strength and hardness than pure copper while retaining its good formability. Brass can be cast, forged, spun, or stamped into various shapes, depending on the composition and manufacturing process used. The addition of lead or silicon to brass can improve its machinability and fluidity during casting, but at the expense of its ductility and toughness.
Bronze:
Bronze is an alloy of copper and other elements such as tin, aluminum, or nickel, which gives it a range of properties and colors. Bronze is harder and more brittle than copper or brass, but it can still be formed into intricate shapes through casting or machining. The specific composition and heat treatment of bronze can affect its formability, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties.
11. Pricing
Brass, bronze, and copper often exist in different grades. Thus, their price usually varies. While their prices may vary based on the alloys, copper is typically more expensive than brass and bronze. The reduction in bronze price may be due to the lower copper content in the alloy. Likewise, brass is the least expensive because it contains more zinc content. Since zinc is cheaper than copper, the price of brass is reduced.

12. Available Alloys
Brass Alloys
The elemental composition of brass gives it the versatility to come in several different alloys. Some of the most popular brass in rapid prototyping include:
Alloy 260. This alloy is also referred to as cartridge brass. It demonstrates excellent cold working characteristics. Thus, Alloy 260 is useful in automobiles, ammunition, hardware, and fasteners.
Alloy 272. Popularly known as yellow brass, alloy 272 has about 33% zinc. It is mainly suitable for industrial applications.
Alloy 330. This brass alloy is valuable in areas where you require high machinability. Its low lead content makes it suitable for cold-working. Many manufacturers choose alloy 330 for piping applications.
Alloy 353. Clock brass helps fabricate high-precision parts like clock parts due to its excellent machinability.
Alloy 360. This is the most common grade of brass available. It shows excellent formability and machinability. Alloy 360 is also very suitable for brazing and soldering applications. In addition, designers and machinists choose this alloy to manufacture fittings, fasteners, valves, and hardware components.
Alloy 464. This alloy is also known as naval brass, and it is famous due to its excellent corrosion resistance. It can also withstand a wide range of temperature changes. The suitability to cold and hot forming processes, bending, soldering, welding, etc., makes it useful for many applications.
Bronze AlloysSeveral bronze alloys are also available based on their composition. The most common grades are:
Alloy 932. Manufacturers employ this high-leaded bronze for making washers, bushings, and other non-pressure components.
Alloy 954. This is an aluminum bronze alloy used for industrial and mounting equipment. It is suitable for use in many environments.
Copper Alloys
Copper material is another useful option in rapid prototyping. Some of the most commonly used copper alloys are:
Alloy 101. This oxygen-free copper is suitable whenever you need high ductility and electrical conductivity.
Alloy 110. Electrolytic (ETP) copper demonstrates the highest thermal and electrical conductivity. It also has excellent ductility and malleability.
Alloy 122. While it is quite similar to Alloy 110 mechanically, it has superior weldability and formability.
Alloy 145. This is tellurium copper. It has about 0.7 percent tellurium content. Like many other copper alloys, it has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, superior machinability, and high formability.
13. Applications
Copper is an exceptional metal with unique properties that make it valuable in various industries. Its thermal and electrical conductivity, superior corrosion resistance, and antibacterial properties make it an ideal material for electronics, medical equipment, plumbing, and roofing applications.
Electrical wiring and electrical machines
Heating and cooling systems
Medical equipment
Plumbing components
Roofing and guttering systems
Decorative pieces, such as sculptures and jewelry.
Brass is a versatile metal alloy composed of copper and zinc, with varying ratios of each material that can create various types of brass. It has a bright gold appearance, making it aesthetically pleasing for decorative purposes. Here are some main uses of brass:
Decorative purposes: Brass is often used in decorative items such as lamps, vases, candle holders, doorknobs, and picture frames. Its elegant golden hue makes it a popular choice for interior designers and home decorators.
Musical instruments: Many musical instruments, especially those in the brass family, are made using brass due to its durability, tonal properties, and ease of fabrication. Trumpets, horns, tubas, flutes, and saxophones are some examples of instruments made with brass.
Plumbing fixtures: Brass is also commonly used in plumbing fixtures as it is highly resistant to corrosion. Components like faucets, valves, and pipes are often made from the material, which ensures the safe transport of water and other fluids.
Electrical fittings: The electrical conductivity of brass makes it an ideal material for use in electrical equipment such as switches, connectors, terminals, plugs, and sockets.
Automotive parts: Brass is also used extensively in the automotive industry for manufacturing parts such as radiators, carburetors, and pumps, thanks to its excellent machinability, resistance to corrosion, and inherent strength.
Ammunition casings: Brass is used readily in producing ammunition casing due to its relatively low price and malleability.

Bronze is an alloy composed primarily of copper with varying amounts of tin, zinc, or other metals. Bronze has been used by humans for thousands of years due to its versatile properties and durability. Some of the main uses of Bronze include:
Sculpture: Bronze’s ability to retain fine details and resistance to corrosion makes it a popular choice of material for creating sculptures.
Tools and Weapons: The hardness and toughness of bronze make it ideal for making tools and weapons such as axes, chisels, knives, swords, spears, etc.
Architecture and Engineering: Bronze has been used in architectural and engineering applications such as bridges, door handles, hinges, hardware, bells, and statues.
Coins: Bronze has been used to mint coins since ancient times due to its durability, malleability, and resistance to corrosion.
Musical Instruments: Bronze alloys are commonly used in the production of musical instruments like cymbals, gongs, bells, and saxophones due to their unique sound qualities.

Brass vs Bronze vs Copper: Which One Should I Choose?
Knowing the difference between brass, bronze, and copper will help you learn how to choose sheet metal for rapid prototyping. The selection process is critical for high-quality results in the design and manufacturing stage. When selecting, you should keep the following in mind:
While the three metals offer increased durability, they do not have the same degree of machinability. You should consider this to ensure smoother machining and cost reduction.
Budget is another crucial consideration. Brass is the cheapest of the three metals, while copper is the most expensive. Therefore, if budget is a concern, you may want to go for brass.
Ultimately, application and utility also come to play in your selection. The eventual use of your component will determine the type of metal you choose. Copper will be beneficial whenever you need electrical conductivity. Bronze s suited for saltwater applications because of its corrosion resistance. It is also durable and hard, and it can withstand fatigue.
CNCMECHA: Manufacturing Metal Parts and Prototypes for You
If you need more information about these metal materials or you are confused about which one to choose, let CNCMECHA help. Having expert advice during material selection gives you the edge over your competition. At CNCMECHA, we boast of the best technicians and professional machinists who will choose the best material for your project.
Additionally, we provide manufacturing and prototyping services, including CNC Machining, Metal fabrication, Aluminum Extrusion, Casting. Contact us today, and let's get started!