Contents
II. CNC Machining Applications
V. 10 common mistakes in CNC machining
VI. Materials and surface treatments common used for machined parts
VII. Tolerance in CNC Machining
VIII. How to control the quality and precise for a part?
X. How to evaluate if your Chinese CNC machining supplier qualified enough or not?
I. Introduction
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) is a technology that has revolutionized machining and manufacturing. The use of CNC machining has significantly increased the accuracy, speed, and consistency of parts production. The history of CNC machining dates back to the 1940s when the first computer for data processing was built. This article aims to explore the evolution of CNC machining, including its process, machinery, tolerance, application, etc.
1. The Early Years of CNC Machining

The first CNC machines were developed in the 1940s and 1950s. These machines were designed as large-scale milling machines that used punched cards to control the movements of the cutting tools. The first CNC machine was developed by John T. Parsons in collaboration with Frank L. Stulen at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
By the 1960s, there was a significant increase in the use of computers in industry. It was during this period that the first CNC systems were developed. These early CNC systems were used for milling, drilling, and grinding operations. They were controlled by numerical controllers that used magnetic tapes or punched cards to store the program instructions.
The 1970s saw significant growth in the development of CNC machining. This period saw the introduction of the first computer-controlled lathes and machining centers. The machines were controlled by mini-computers that enabled them to perform complex operations.
In the 1980s, personal computers became more affordable, and this made it easier for small businesses to invest in CNC machines. During this period, CNC machines began to be used extensively in the automotive and aerospace industries.
2. Modern CNC Machining
Today, CNC machines have become an essential part of modern manufacturing processes. They are used in a wide range of applications, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics industries. Modern CNC machines are highly advanced, with the ability to perform complex operations with great precision and accuracy.
China has been a major player in the global manufacturing industry for decades, and the development of CNC machining has played a significant role in this success. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled machines to produce precise and complex parts and components. The technology has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, and China has been at the forefront of its development.
II. CNC Machining Applications
CNC machining is used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics. The following are some of the common applications of CNC machining:
Aerospace: CNC machining is used to create complex components for aircraft engines, landing gear, and other critical systems.
Automotive: CNC machining is used to create engine components, suspension systems, and other parts used in vehicles.
Medical: CNC machining is used to create surgical instruments, dental implants, and orthopedic components.
Electronics: CNC machining is used to create printed circuit boards (PCBs), connectors, and other electronic components.
III. CNC Machining Machinery
There are several types of CNC machines, including lathes, mills, routers, and grinders. Each type of machine is designed to perform specific operations.
Lathes: CNC lathes are designed for turning operations. They are used to create cylindrical parts such as shafts, pins, and bushings.
Mills: CNC mills are designed for milling operations. They are used to create complex shapes and features, including pockets, holes, and slots.
Routers: CNC routers are designed for cutting wood, plastic, and other soft materials. They are commonly used in the sign-making industry.
Grinders: CNC grinders are designed for grinding operations. They are used to create precise surfaces and finishes on parts.
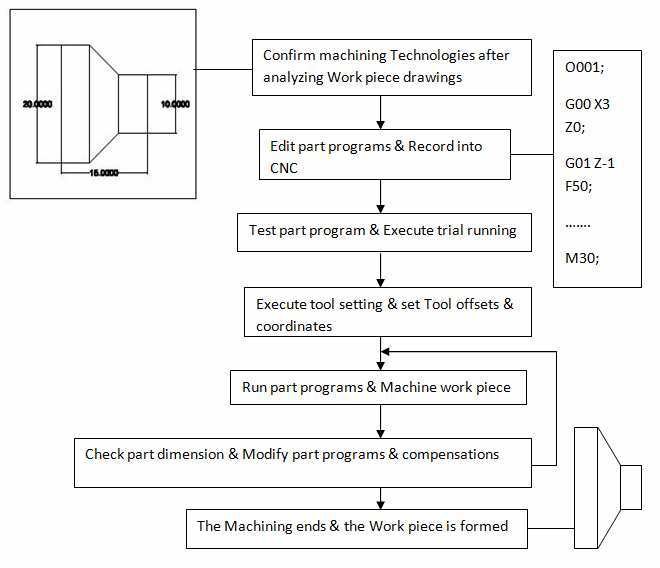
IV. The CNC Machining Process
The CNC machining process involves several steps, including designing, programming, and machining. The process begins with the design of the part or component, which is created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The CAD file is then converted into a CNC program, which contains the instructions for the cutting tool to follow.
Once the program is created, the CNC machine is set up for the machining process. This involves attaching the workpiece to the machine and positioning the cutting tool in the correct location. The machine is then programmed to follow the instructions in the CNC program, which directs the cutting tool to move along multiple axes to create the desired shape and size.
During the machining process, the cutting tool removes material from the workpiece, creating chips that are removed by the machine's coolant system. The machine continuously monitors the cutting process, making adjustments as needed to ensure that the part or component is produced to the desired specifications.
CNC milling and CNC turning are two of the most common types of CNC machining processes.
CNC Milling
CNC milling is a process that uses a rotating cutting tool to remove material from a workpiece. The cutting tool is controlled by a computer program, which directs it to move along multiple axes to create the desired shape and size. CNC milling is commonly used to create complex parts with high precision and accuracy. It is often used in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries, among others.
CNC milling machines can be classified into two main types: vertical and horizontal. Vertical milling machines have a vertical spindle axis, which allows for the creation of complex shapes and contours. Horizontal milling machines have a horizontal spindle axis, which is ideal for creating flat surfaces and cutting slots and grooves.
CNC Turning
CNC turning is a process that uses a rotating workpiece and a stationary cutting tool to remove material from the workpiece. The cutting tool is controlled by a computer program, which directs it to move along multiple axes to create the desired shape and size. CNC turning is commonly used to create cylindrical parts, such as shafts, bolts, and screws. It is often used in the automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing industries.
CNC turning machines can be classified into two main types: horizontal and vertical. Horizontal turning machines have a horizontal spindle axis, which is ideal for creating cylindrical parts. Vertical turning machines have a vertical spindle axis, which is ideal for creating large, heavy parts.
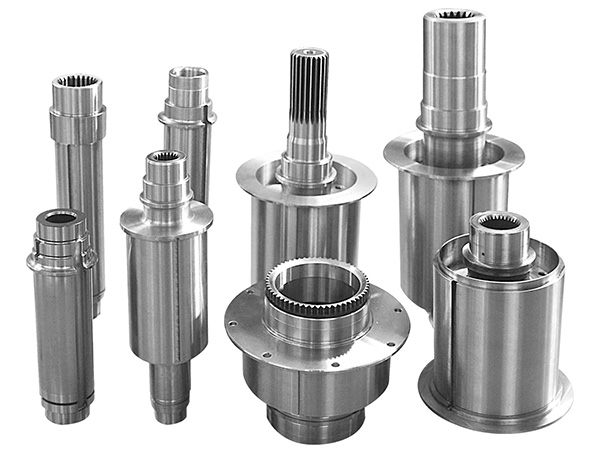

V. 10 common mistakes in CNC machining.
Incorrect Tool Selection: Choosing the wrong tool for the job can lead to poor surface finish, tool breakage, and longer machining times. It is important to select the appropriate tool for the material being machined and the desired finish.
Improper Feeds and Speeds: Incorrect feeds and speeds can lead to poor surface finish, tool breakage, and longer machining times. It is important to use the correct feeds and speeds for the material being machined and the tool being used.
Poor Fixturing: Poor fixturing can lead to inaccurate machining and poor surface finish. It is important to properly secure the workpiece to the machine bed and ensure that it is properly aligned.
Incorrect Programming: Incorrect programming can lead to inaccurate machining and poor surface finish. It is important to carefully review the program before running the machine to ensure that it is correct.
Lack of Maintenance: Neglecting to maintain the machine and tools can lead to poor performance and premature wear. It is important to regularly clean and lubricate the machine and tools, and to replace worn or damaged parts as needed.
Inadequate Inspection: Failing to inspect the workpiece during and after machining can lead to errors and poor quality. It is important to regularly inspect the workpiece to ensure that it is being machined to the desired specifications.
Poor Communication: Poor communication between the machinist and other members of the production team can lead to errors and delays. It is important to communicate clearly and effectively with all members of the team to ensure that everyone is on the same page.
Incorrect Tool Path: Incorrect tool path can lead to poor surface finish, tool breakage, and longer machining times. It is important to carefully plan the tool path to ensure that it is efficient and accurate.
Overcutting: Overcutting can lead to poor surface finish and inaccurate machining. It is important to carefully plan the depth of cut to ensure that it is appropriate for the material being machined.
Undercutting: Undercutting can lead to poor surface finish and inaccurate machining. It is important to carefully plan the tool path to ensure that the tool does not undercut the workpiece.
CNCMECHA has dedicated to CNC machining for years. We know a lot about how to communicate with the factories in China and control the quality properly. We help you source the right CNC factories with reliable quality, to lower your risks, save your time, and reduce your ultimate total cost. Choose CNCMECHA to make your CNC parts at the top-notch. SEND AN ENQUIRY
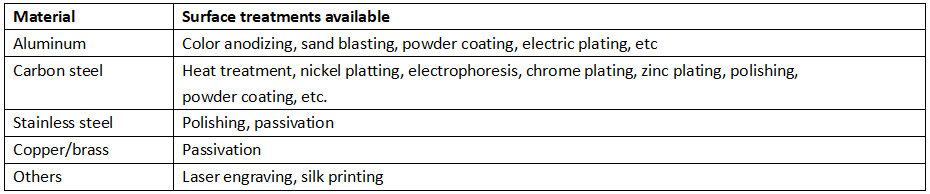
VI. Materials and surface treatments common used for machined parts.
There are several materials that can be used in CNC machining, each with its own unique properties and advantages.
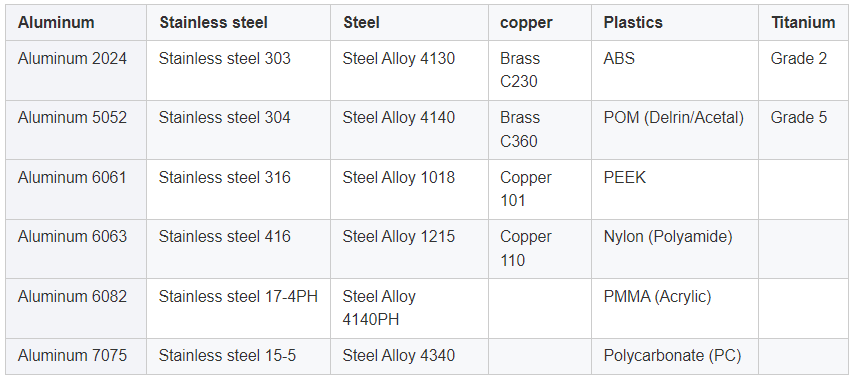
Metals: Metals are the most commonly used materials in CNC machining. They are strong, durable, and can withstand high temperatures and pressures. Some of the most commonly used metals in CNC machining include aluminum, brass, copper, steel, and titanium. Each metal has its own unique properties, such as strength, corrosion resistance, and conductivity, which make them suitable for different applications.
Plastics: Plastics are lightweight, flexible, and easy to shape, making them ideal for CNC machining. Some of the most commonly used plastics in CNC machining include acrylic, polycarbonate, nylon, PEEK, ABS, and PVC, etc. Please click HERE to read more about plastic materials. Plastics are often used in applications where weight is a concern, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Composites: Composites are materials made from two or more different materials that are combined to create a new material with unique properties. Composites are often used in CNC machining because they are lightweight, strong, and durable. Some of the most commonly used composites in CNC machining include carbon fiber, fiberglass, and Kevlar.
Wood: Wood is a natural material that is often used in CNC machining to create decorative and functional parts. Wood is easy to shape and can be finished in a variety of ways to create a unique look and feel. Some of the most commonly used woods in CNC machining include oak, maple, and cherry.
Ceramics: Ceramics are hard, brittle materials that are often used in CNC machining to create parts that require high levels of precision and durability. Some of the most commonly used ceramics in CNC machining include alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide.
The choice of material will depend on the specific application and the desired properties of the finished product. By understanding the properties of different materials, manufacturers can choose the best material for their CNC machining needs and create high-quality, precise parts and components.
Surface treatments common used on machined parts. SEND A RFQ

VII. Tolerance in CNC Machining
Tolerance in CNC machining refers to the allowable deviation from the desired dimensions of a part or component. Tolerance is an important consideration in CNC machining, as it determines the accuracy and precision of the final product. The tolerance in CNC machining can vary depending on the material being machined, the complexity of the part, and the desired finish.
The tolerance in CNC machining can be affected by several factors, including the accuracy of the machine, the quality of the tooling, the rigidity of the workholding, and the skill of the machinist. It is important to carefully consider these factors when selecting a CNC machining service provider to ensure that the desired tolerance can be achieved.
Different levels of tolerance that can be specified for CNC machining. These include:
Standard Tolerance: The standard tolerance is typically expressed in thousandths of an inch (or microns for metric measurements) and is +/- 0.005 inches (or +/- 0.127 mm) for most materials.
This means that the final dimensions of the part may vary by up to 0.005 inches (or 0.127 mm) from the desired dimensions. The standard tolerance is suitable for most CNC machining applications, including those that require a high degree of accuracy and precision.
Tight Tolerance: The tight tolerance in CNC machining is typically expressed in thousandths of an inch (or microns for metric measurements) and can range from +/- 0.001 inches (or +/- 0.025 mm) to +/- 0.0001 inches (or +/- 0.0025 mm) or even tighter, depending on the specific application, such as aerospace or medical components.
Loose Tolerance: This is a lower level of tolerance that is used for less critical applications, such as decorative or non-functional parts.
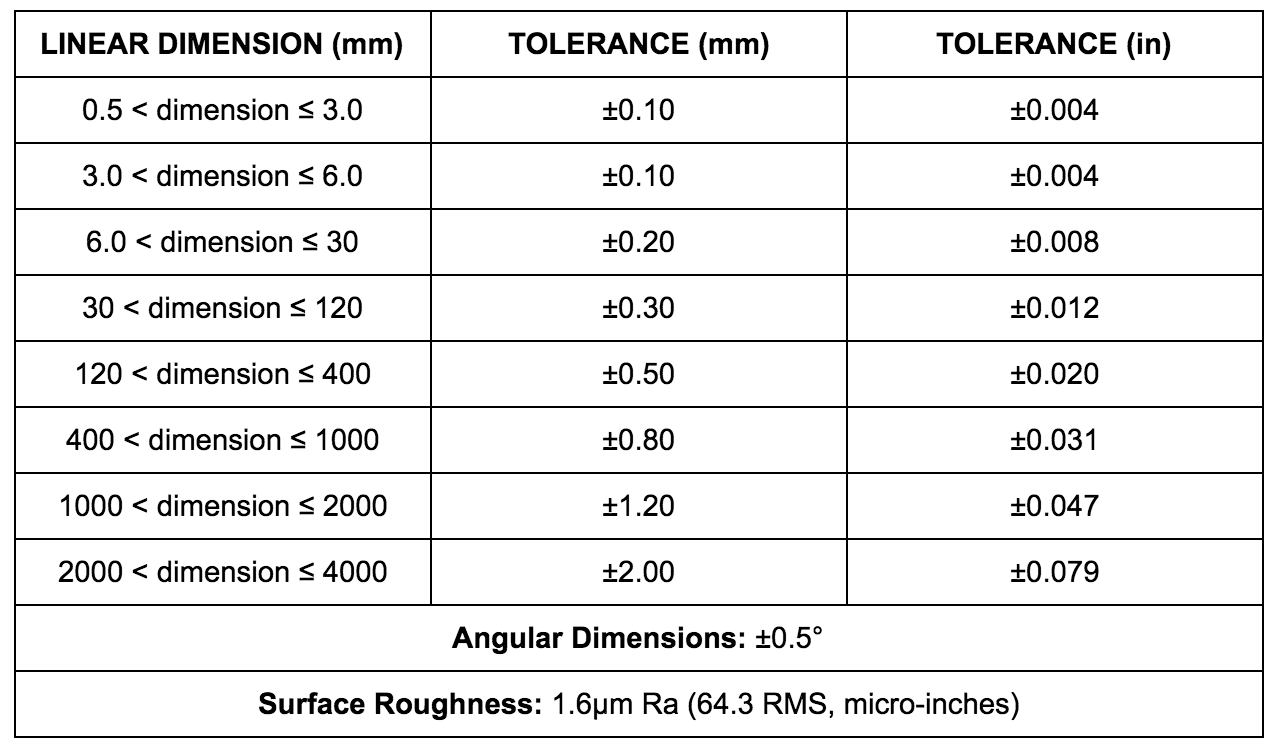
It is important to specify the desired tolerance when submitting a design for CNC machining to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications.
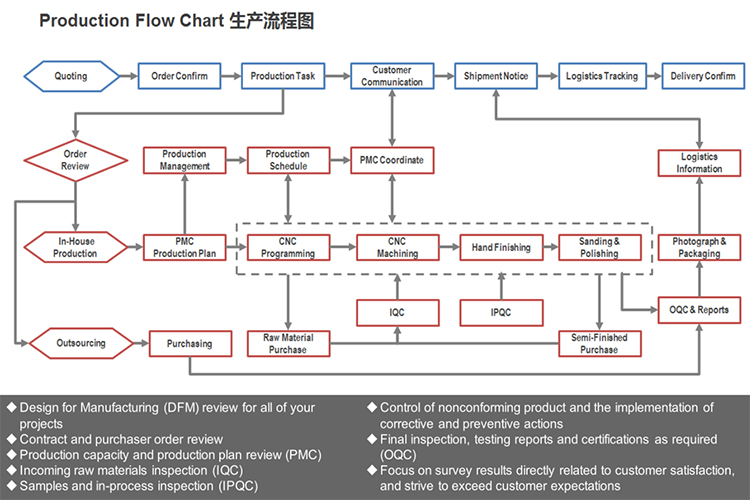
VIII. How to control the quality and precise for a part?

Controlling the quality and precision of CNC machining involves several steps, including:
Design: Ensure that the design of the part or component is accurate and precise, with clear specifications for dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes.
Material selection: Choose high-quality materials that are suitable for the intended application and have consistent properties.
Machine calibration: Regularly calibrate the CNC machine to ensure that it is operating within the specified tolerances and that all axes are properly aligned.
Tool selection: Use appropriate cutting tools that are sharp, properly sized, and designed for the specific material being machined.
Programming: Carefully program the machining operations, taking into account the material properties, tooling, and desired tolerances.
Inspection: Inspect the machined parts at various stages of the process to ensure that they meet the specified tolerances and surface finishes.

Documentation: Keep detailed records of the machining process, including the design specifications, material selection, machine calibration, tooling, programming, and inspection results.
By following these steps, you can ensure that CNC machining produces high-quality, precise parts and components that meet the desired specifications and perform as intended.
Any questions or concerns about our quality control system, please leave us a message.
VIIII. CNC machining in China
The history of CNC machining in China dates back to the 1970s when the country began to invest heavily in its manufacturing industry. At that time, China was primarily focused on producing low-cost, low-tech products, but the government recognized the need to upgrade its manufacturing capabilities to remain competitive in the global market. CNC machining was seen as a key technology that could help China achieve this goal.
In the early days, China relied heavily on imported CNC machines and technology from countries like Japan and Germany. However, the country soon began to develop its own CNC machines and software, and by the 1990s, China had become a major producer of CNC machines.
One of the key factors that contributed to the development of CNC machining in China was the country's large pool of skilled labor. China has a long tradition of manufacturing, and the country's workforce is known for its technical expertise and attention to detail. This made it easier for Chinese manufacturers to adopt and adapt to the new technology.
Another factor that contributed to the development of CNC machining in China was the government's support for the industry. The Chinese government provided funding and incentives to encourage the development of CNC technology, and this helped to create a favorable environment for manufacturers to invest in the technology.
Today, China is one of the world's leading producers of CNC machines and components. The country's CNC industry has grown rapidly over the past few decades, and Chinese manufacturers are now able to produce high-quality, precision parts and components at a lower cost than many of their competitors.
The development of CNC machining in China has had a significant impact on the country's economy. The technology has helped to create new jobs and industries, and it has also helped to improve the quality and efficiency of Chinese manufacturing. As China continues to invest in CNC technology and other advanced manufacturing processes, it is likely that the country will remain a major player in the global manufacturing industry for years to come.

X. How to evaluate if your Chinese CNC machining supplier qualified enough or not?
There are thousands suppliers in China, sometimes it's a challenge task for a foreign customer to select the suitable one among them. Below are several factors to consider when looking for a reliable CNC machining supplier, including:
Experience: Look for a supplier with extensive experience in CNC machining, as this indicates that they have the knowledge and expertise to produce high-quality parts.
Quality control: Choose a supplier that has a robust quality control process in place, including inspection and testing at various stages of the machining process.
Equipment: Ensure that the supplier has modern, well-maintained CNC machines and cutting tools that are capable of producing precise, accurate parts.
Materials: Look for a supplier that uses high-quality materials that are suitable for the intended application and have consistent properties.
Customer service and communication are critical components of CNC machining, as they can help ensure that the final product meets the customer's needs, is delivered on time, and is cost-effective. They can impact the quality, cost, and timeliness of the final product.
Here are some reasons why customer service and communication are important.
Clarifying requirements: Effective communication with the supplier can help clarify the design requirements, material specifications, and tolerances needed for the part or component. This can help ensure that the final product meets the customer's needs and expectations.
Problem-solving: Good customer service can help resolve any issues or problems that arise during the machining process, such as unexpected delays or quality issues. This can help minimize the impact on the project timeline and budget.
Timeliness: Clear communication with the supplier can help ensure that the machining process stays on schedule and that the final product is delivered on time.
Cost-effectiveness: Effective communication with the supplier can help identify opportunities to reduce costs, such as by optimizing the machining process or selecting more cost-effective materials.
Building relationships: Good customer service and communication can help build a strong relationship between the customer and the supplier, which can lead to future business opportunities and a more collaborative working relationship.
The core value of CNCMECHA is keep providing qualified parts, delivery on time, make the customer satisfied, help our customers time saving, and work easy.
Thanks for your reading!
by Karen Xia